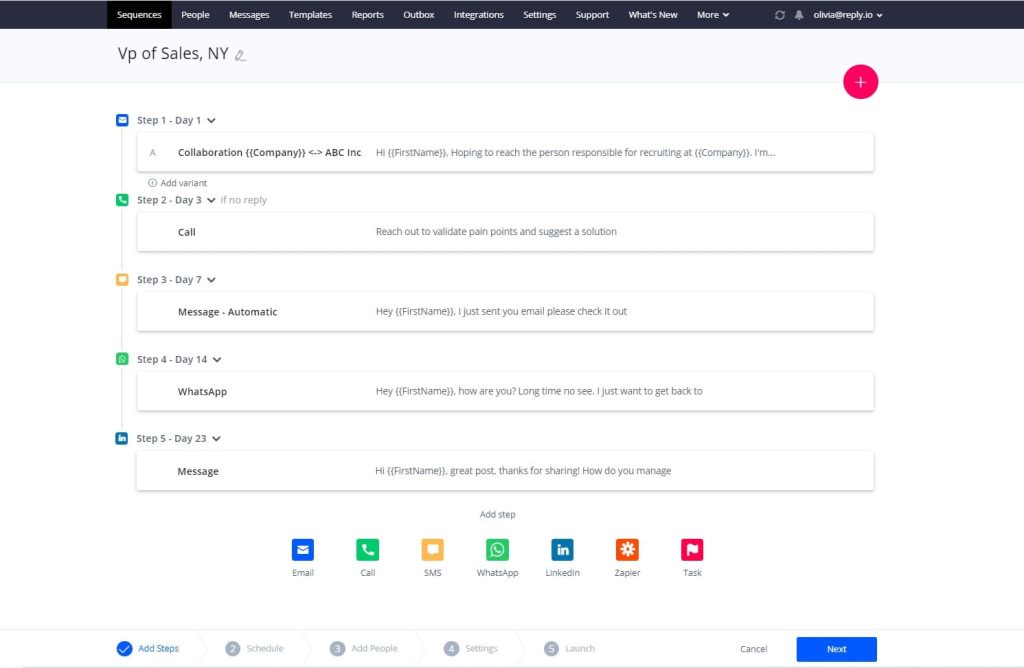
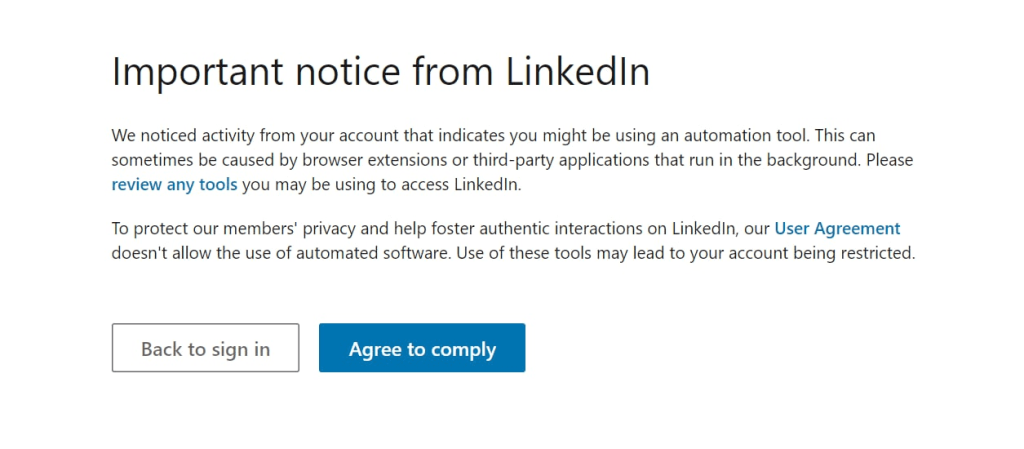
Whether you’re in sales, marketing, business development, partnerships, or HR, it’s safe to assume that you use LinkedIn one way or the other, especially if you work in B2B.
What started off as a simple social platform for professionals, LinkedIn has become one of the most powerful tools for networking, prospecting, and outreach in 2025. With over 900 million users, chances are that your target prospects, partners, or talents already have profiles on this social platform.
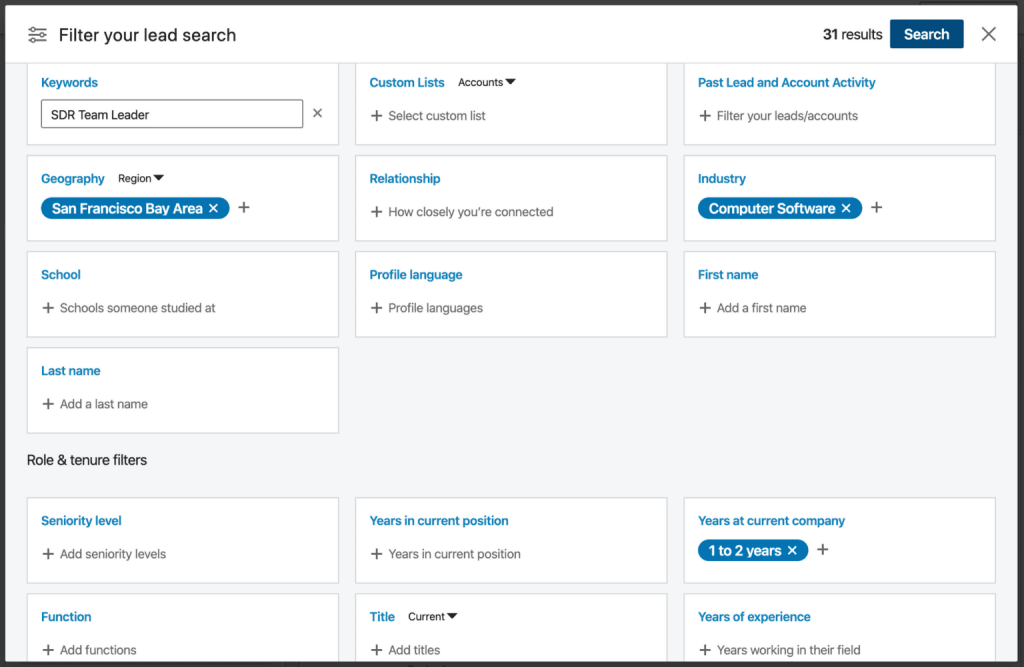
Moreover, these profiles contain valuable information about prospects and their companies that sales and marketing teams can leverage to identify targeted leads, determine the best time and message to engage with them and explore potential ways to personalize communication.
However, going through thousands of profiles and sourcing relevant prospect data manually can take ages, and that’s where LinkedIn scrapers come into play.
In this article, we’ll take a closer look at how LinkedIn scraping works and how businesses can leverage this powerful tool to supercharge their prospecting and outreach efforts in 2025.
LinkedIn scraping 101: What is it?
Let’s start with the basics—what is LinkedIn scraping?
In essence, LinkedIn scraping involves automatically collecting structured information from personal profiles and company pages on LinkedIn.
To do this, businesses use various LinkedIn scrapers, which are different types of software designed to automatically extract relevant data from LinkedIn profiles, including job titles, company information (name, size, industry, revenue), and, most importantly—contact data like emails and phone numbers.
This way, businesses can significantly expand their contact lists with targeted prospects much quicker, increasing the audience for their sales and marketing efforts.
There are myriad types of LinkedIn scrapers aimed at different levels of technical expertise and business needs, but all of them can be split into three main categories:
- Cloud-based: These LinkedIn scrapers are built on APIs, hence requiring no software installation from the user’s end. They are quite hassle-free, suitable for large-scale scraping, and are usually accompanied by extra features such as data enrichment.
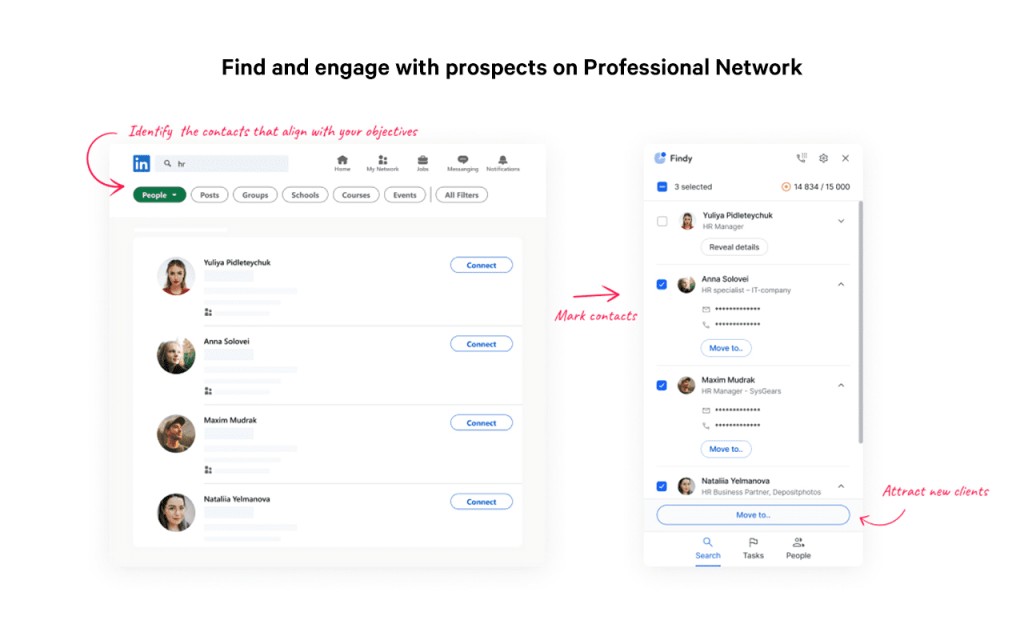
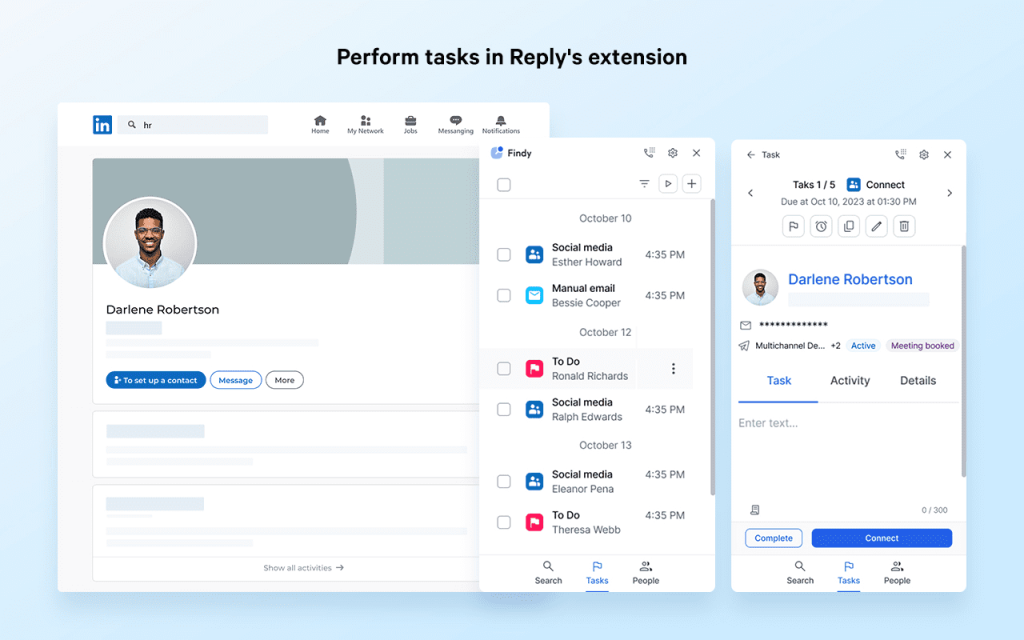
- Browser-based: Such scrapers work through browser extensions and actually scrape the data in real time when users browse LinkedIn profiles. They are easy to install and use, and hence, teams of smaller sizes or individual sales/marketing professionals usually find them the most convenient.
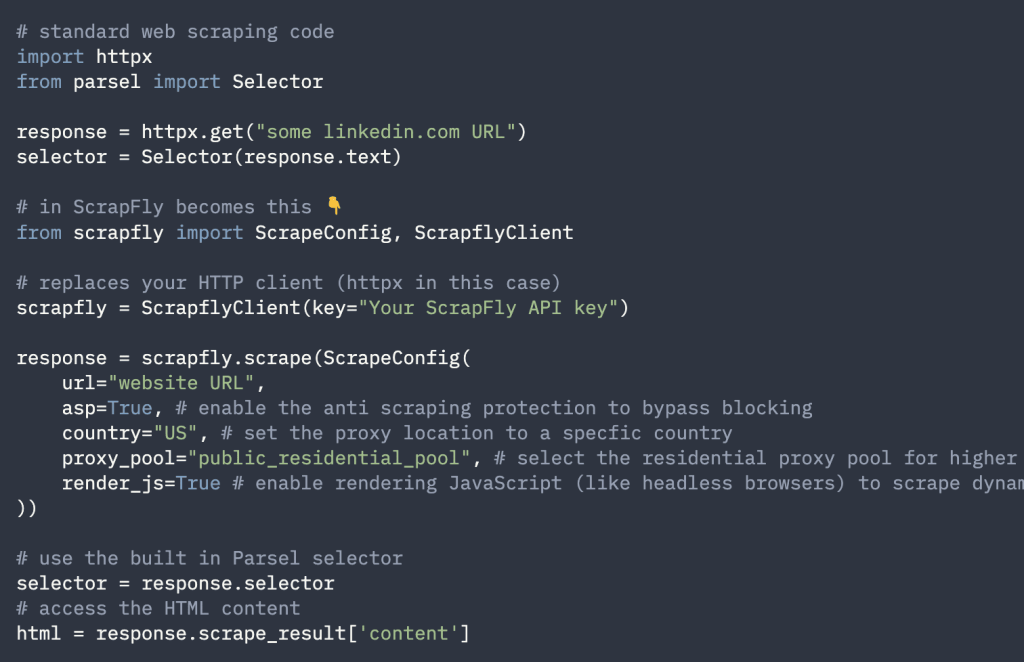
- Desktop-based: Normally, these involve a certain level of coding, such as Python scripts. Users can tailor desktop-based scrapers to their exact business needs, which are often accompanied by extensive data extraction capabilities but also require technical skills to set up and maintain.
Regardless of which tool you use for scraping data, keep in mind that LinkedIn is a powerful B2B tool that can be leveraged in many ways to grow your brand, generate leads, and increase sales.