Sales collateral is the key to moving prospects through the sales funnel.
By developing effective marketing collateral, you’re providing potential clients or customers with the information they need to make a purchase decision.
Read on to learn how you can incorporate collaterals into your sales process and the top types of sales collateral to use.
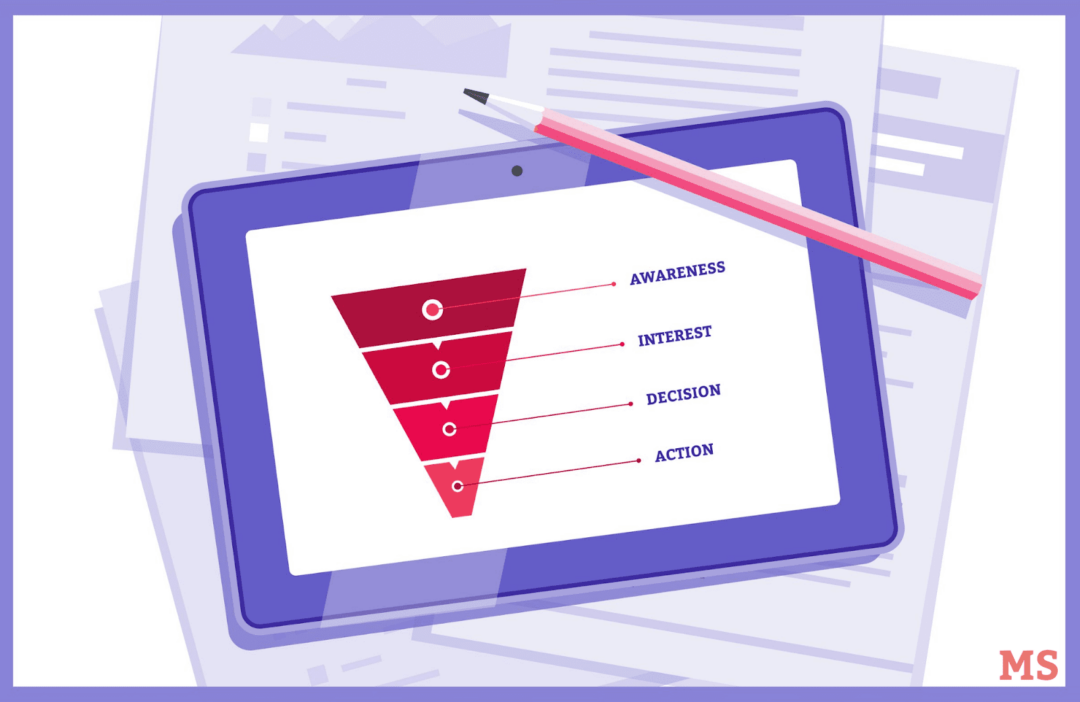
What Are the Stages of Awareness?
Whether it’s an impulse buy or a carefully researched investment, every purchase goes through a series of phases. The buyer journey can vary in length and complexity, but a prospect will typically progress from early awareness to the purchase and even post-purchase stage.
You can conceptualize this journey by identifying the different stages buyers go through. There are various models you can use.
Seven-Step Model
This complex model makes sense for nonlinear buyer journeys that involve multiple decision-makers.
- Initiative. An event triggers the start of the journey. It’s usually a realization that the buyer needs to address an issue. Some buyers will conduct internal research at this stage and set a budget for the purchase or identify the goals they want to achieve.
- Research. Research is a key buying activity. Independent research conducted online represents 27% of the B2B buyer journey, and offline research represents 18%. There might be an initial contact with your organization at the end of this stage with a request for a proposal.
- Assessment. During this stage, prospects will look at the different solutions they identified during the research phase. They will compare these options and measure them against their established requirements to narrow down their list of options.
- Decision. Buyers might seek more information at this stage. They will decide if your solution is the right fit.
- Implementation. Once buyers have picked a solution, they will plan for the purchase and for rolling out the new product, often with the help of the vendor.
- Support. Implementing a new solution can be disruptive. As a vendor, you have an important part to play by providing support to help the buyer achieve their goals.
- Renewal. The last phase of the buyer journey is about customer lifecycle management. You have established an ongoing relationship with the buyer and keep providing support or upgrades. Eventually, the buyer might purchase a new solution from you if they need change.
Five-Step Buyer Journey
This model is more straightforward, might make more sense for selling consumer products, and can be used as a starting point for mapping the customer journey that is unique to your audience.
- Awareness. The buyer becomes aware of your brand or product or aware that there is an issue they need to address.
- Consideration. The prospect will learn more about the product through online research or by contacting a salesperson. They might look at the price, weigh the pros and cons, and compare it to other options.
- Decision. Is the product a good fit? Does it help the buyer achieve their main goals? The buyer will decide whether they want to purchase the product during this crucial stage.
- Retention. The buyer might make another purchase and eventually turn into a repeat customer during this stage.
- Advocacy. With this model, the last stage is advocacy, where the customer becomes loyal to the brand and encourages others to try products through word-of-mouth marketing.