Virtually all businesses use emails one way or another to engage with their existing and potential customers, whether it’s to share promotional materials or schedule a demo.
Therefore, a lot of responsibility lies on the shoulders of these simple emails—they could trigger the beginning of a future sale and drive retention, or they could result in your company’s domain going right into spam, preventing you from ever reaching out to them in the future.
But all those scenarios are only possible if your emails actually get delivered in the first place, meaning they reach their recipients’ primary inboxes.
The giant ESPs (email service providers) like Gmail, Outlook, and Yahoo have been increasingly ramping up their email-sending policies, especially in the context of high-volume emails that businesses operate with.
They do this to protect their users from the growing number of malicious and spam emails that travel through the web, and while that’s great news, unfortunately, businesses that are not careful run the risk of getting their emails flagged as well.
This is where email authentication protocols like DMARC come into play, playing a crucial role in ensuring that your emails remain compliant and legitimate in the eyes of email providers.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll take a closer look at one of the three main authentication protocols — DMARC, and explain what it is, how it works, and how to monitor it in light of the growing email-sending policies in 2025.
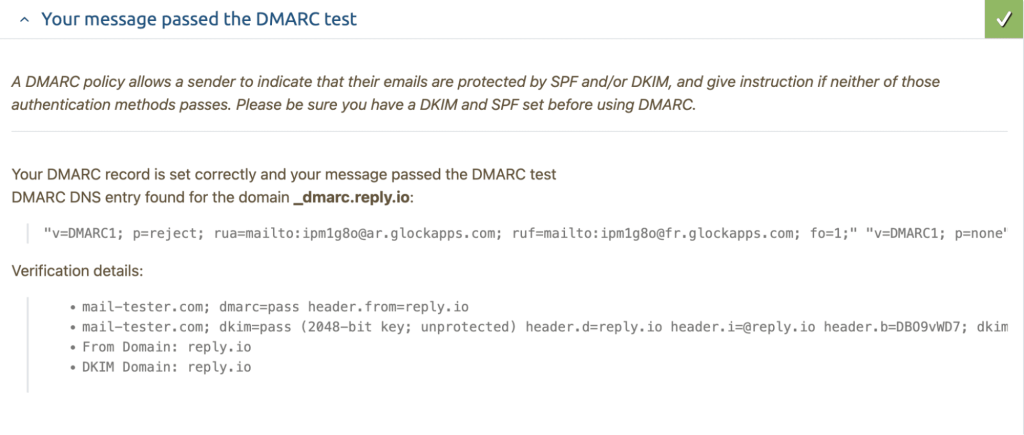
What is the DMARC record?
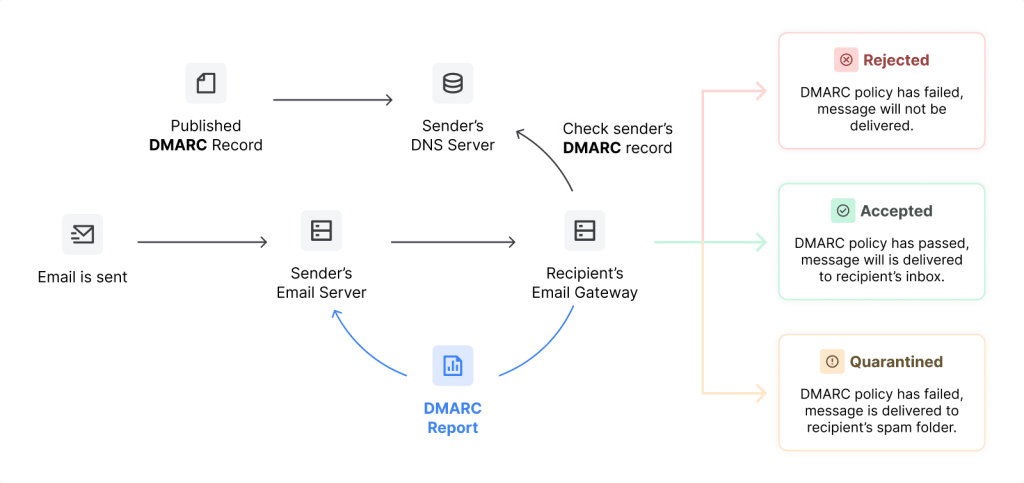
Without getting too technical, a DMARC record (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance), is an email authentication protocol that determines what happens to an email should it fail authentication tests during sending.
Most important of all, DMARC enforces the linking of all these mechanisms together by requiring domain alignment — this means that the domain shown in the “From” line of an email matches with the domains that were validated in the SPF and DKIM sections.
To better understand DMARC and its impact on email deliverability, let’s take a quick look at the SPF and DKIM authentications:
SPF and DKIM both work in combination to provide email authentication, but they are separate mechanisms. DMARC came to solve this challenge by combining the best of both to ensure the email’s “From” domain conforms to the domains being authenticated.
In simple terms, while SPF and DKIM are the foundation of email authentication, DMARC’s mission is to align the two and set up the procedure for sending and receiving should they fail to pass those two authentication tests.
DMARC acts as the final piece in the chain of email authentication protocols, not only improving email deliverability by giving your emails and domain a stamp of legitimacy but also protecting businesses from all sorts of email fraud.
Why is the DMARC check important?
The importance of DMARC and other email authentication procedures simply cannot be brushed off in 2025—they have the potential to determine the success of your business email communications, hence having a direct impact on prospecting, lead generation, customer acquisition, and revenue.
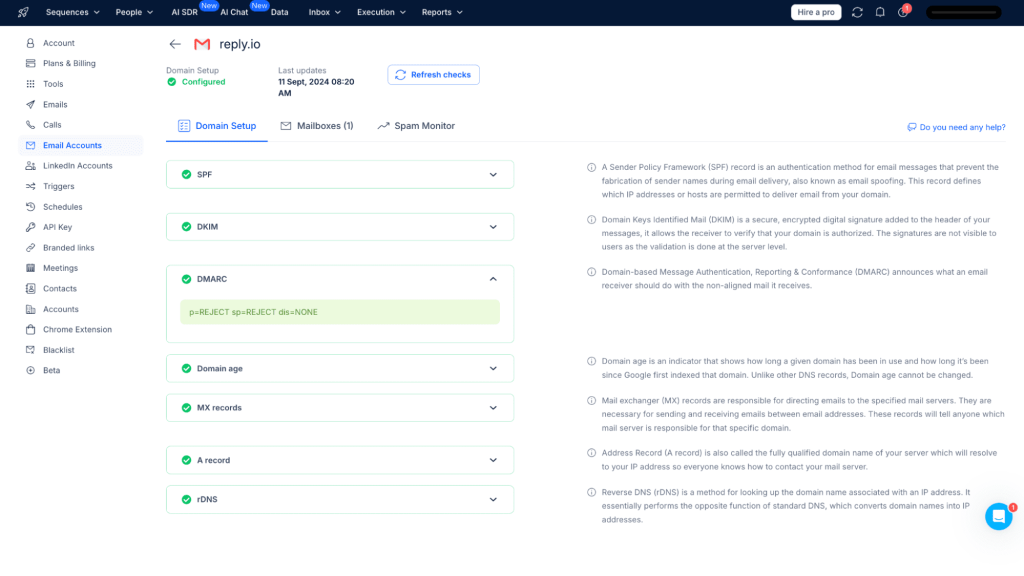
The biggest advantage of DMARC is its direct impact on email deliverability. In light of Google’s new 2025 security policies, email authentication has become a crucial element for ensuring your email campaigns reach their audience.
Businesses that fail to correctly set up all the email authentications, including but not limited to SPF, DKIM, and DMARC will be much more likely to be grouped with malicious and spam email senders, and therefore flagged as spam, potentially blacklisting your business domain.
This rule goes double for businesses and individuals sending 5k+ emails per day, so if we think in the context of email newsletters, marketing promos, and sales engagement campaigns, authentication has never been more important than now.
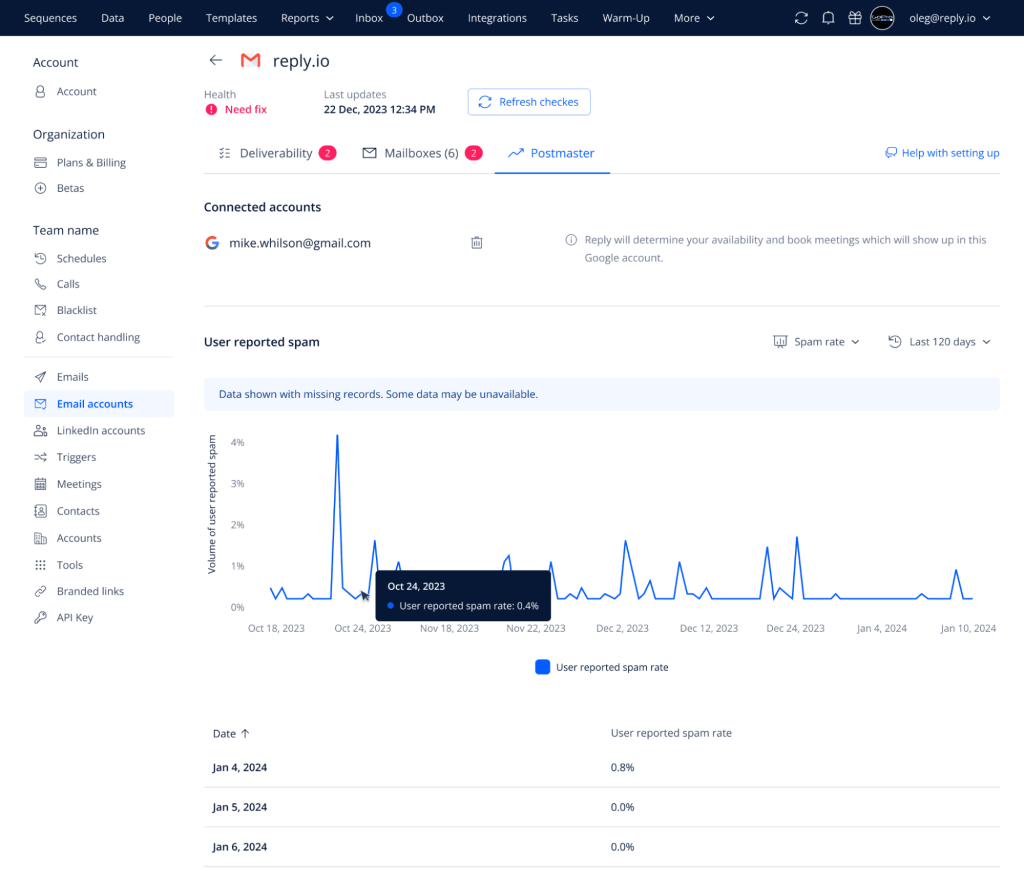
DMARC is the final nail in your email authentication, significantly decreasing the chances of your email correspondence getting rejected by email servers or getting flagged as spam. With the new strict 0.3% spam rate threshold recently announced by Google.
On top of that, DMARC builds your company’s sender reputation by only allowing authenticated emails to be delivered from your end. On the other hand, a weak sender reputation, caused by emails being regularly flagged as suspicious, has long-term effects on your business because it’s very challenging to recover your email domain.
The solution? Properly set up and maintain your DMARC records to avoid these issues from ever occurring in the first place.